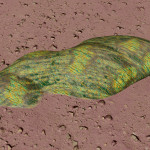
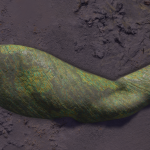
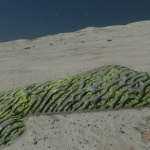
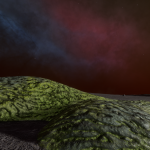
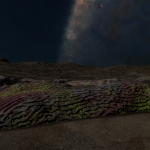
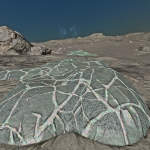
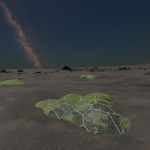
Stratum genus
Description
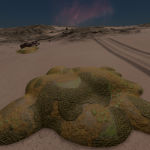
Low-lying photosynthetic organisms that bond tightly to the surface of rocks. The body of the organism may be embedded in the rock subsurface to provide protection from the elements, leaving the tough photosynthetic proto-leaves exposed. Their simple proto-evolutionary nature means that they are a common sight on rocky worlds. Colouration is driven by a mixture of the mineral content of the attached rock and the absorption spectral of the nearby stellar body.
Minimum distance between two genetic samples: 500 m
Conditions of occurrence:
- Planets with thin atmosphere
- Rocky or High Metal Content planets
- Mean temperature superior to 165 K
| Planet type | Atmosphere type | Species |
|---|---|---|
| High Metal Content | Oxygen Ammonia Water, Water-rich Carbon dioxide Carbon dioxide rich Sulphur dioxide | Stratum tectonicas (> 165 K) |
| Rocky | Ammonia | Stratum paleas (> 165 K) Stratum laminamus (> 165 K) |
| Water, Water-rich | Stratum paleas | |
| Carbon dioxide Carbon dioxide rich | Stratum paleas (> 165 K) Stratum excutitus (165 K - 190 K) Stratum limaxus (165 K - 190 K) Stratum frigus (> 190 K) Stratum cucumisis (> 190 K) |
|
| Sulphur dioxide | Stratum araneamus (> 165 K) Stratum excutitus (165 K - 190 K) Stratum limaxus (165 K - 190 K) Stratum frigus (> 190 K) Stratum cucumisis (> 190 K) |
Colored variants
Colored variant determined by the parent star type:
| Star type | Color |
|---|---|
| O | |
| B | |
| A | |
| F | Emerald |
| G | |
| K | Lime |
| M | Green |
| L | |
| T | Grey |
| TTS | Amethyst |
| Y | |
| W | |
| D | Mauve |
| N |
Stratum araneamus
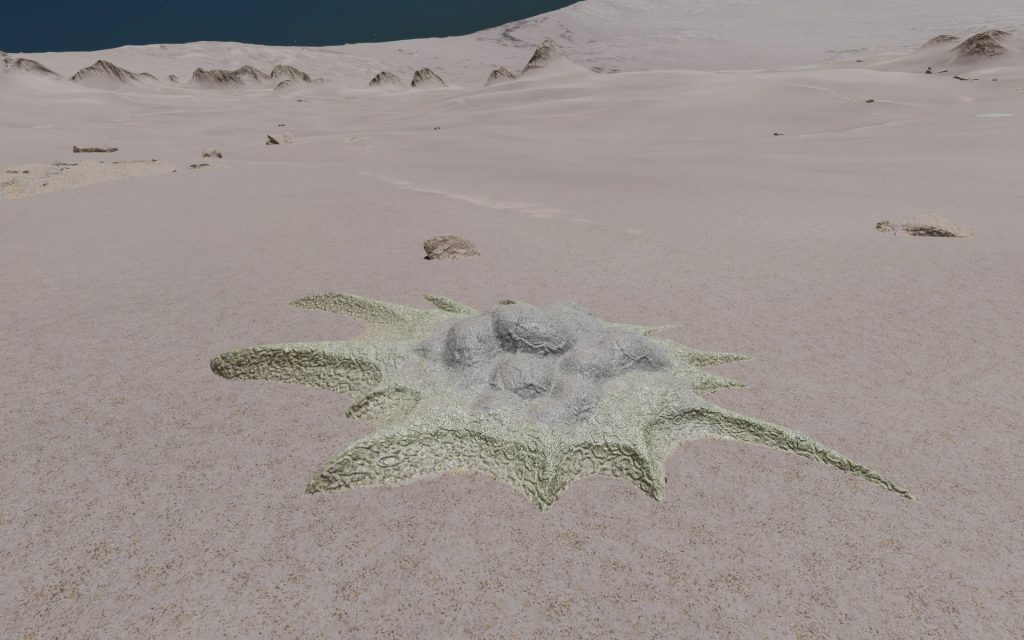

Description
A stratum species that has a vaguely octopoid shape. Their pale semi-translucent upper domes can reveal colourful inner organisms, which contrast with their darker outstretched tentacles.
Conditions of occurrence
- Planets with thin Sulphur dioxide atmosphere
- Rocky planets
- Mean temperature superior to 165 K
| Planet type | Atmosphere type | Species |
|---|---|---|
| High Metal Content | Oxygen Ammonia Water, Water-rich Carbon dioxide Carbon dioxide rich Sulphur dioxide | Stratum tectonicas (> 165 K) |
| Rocky | Ammonia | Stratum paleas (> 165 K) Stratum laminamus (> 165 K) |
| Water, Water-rich | Stratum paleas | |
| Carbon dioxide Carbon dioxide rich | Stratum paleas (> 165 K) Stratum excutitus (165 K - 190 K) Stratum limaxus (165 K - 190 K) Stratum frigus (> 190 K) Stratum cucumisis (> 190 K) |
|
| Sulphur dioxide | Stratum araneamus (> 165 K) Stratum excutitus (165 K - 190 K) Stratum limaxus (165 K - 190 K) Stratum frigus (> 190 K) Stratum cucumisis (> 190 K) |
Colored variants
Colored variant determined by the parent star type (see above, genus Stratum)
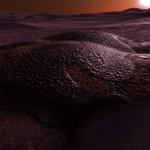
Stratum cucumisis
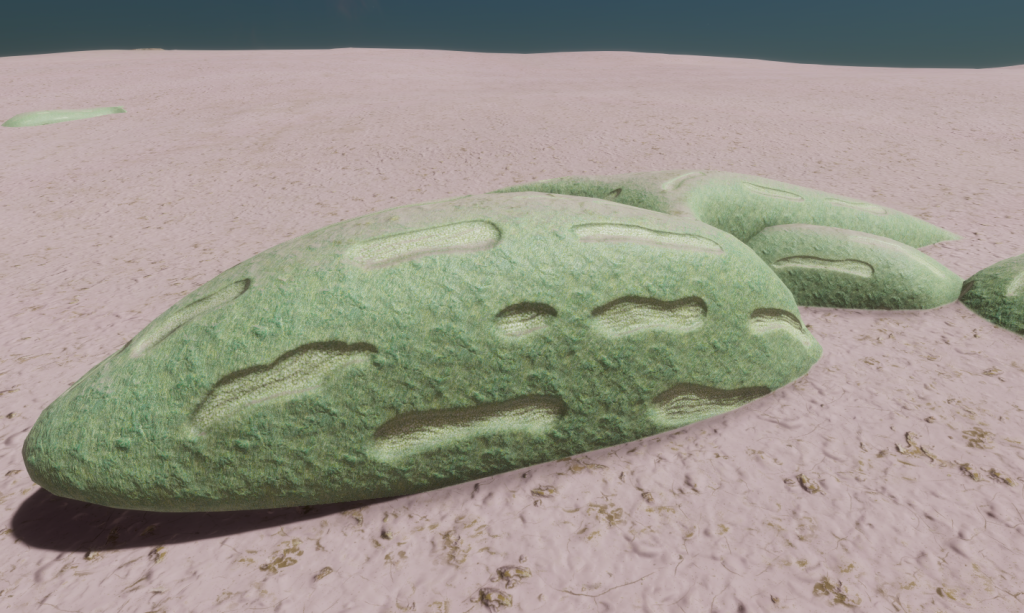

Description
A species of stratum that displays fleshy ovoid shapes that are connected in a narrow pattern across the ground. These are covered with streaks of round photosynthetic cells that absorb sunlight.
Conditions of occurrence
- Planets with thin Sulfur dioxide or Carbon dioxide atmosphere
- Rocky planets
- Mean temperature superior to 190 K
Colored variants
Colored variant determined by the parent star type (see above, genus Stratum)
Stratum excutitus
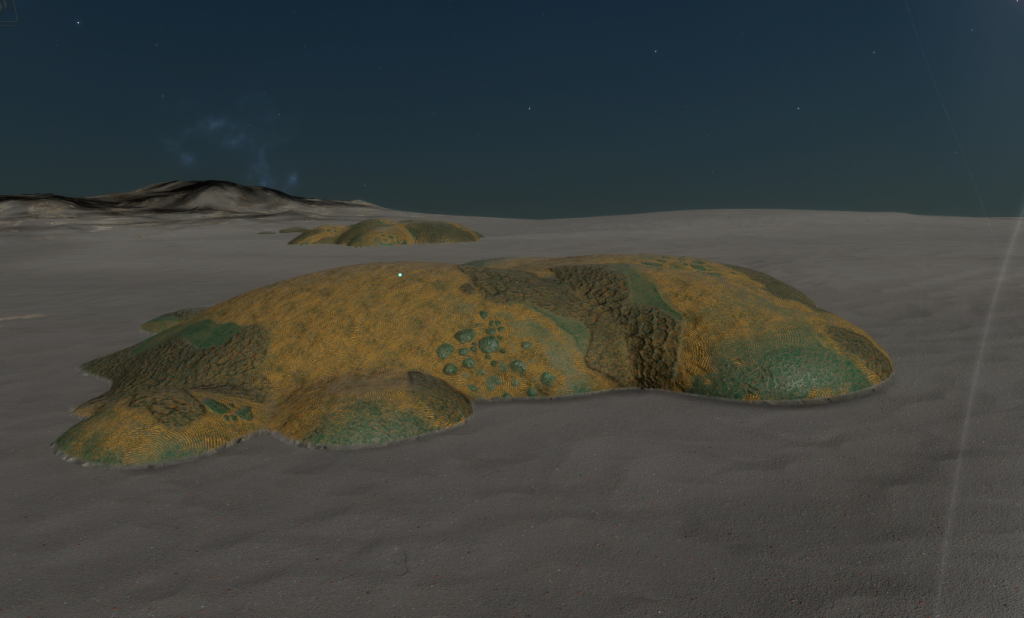
Description
This stratum species appears as a mixture of tight concentric ring patterns and mottled proto-leaves in a mixture of dark hues.
Conditions of occurrence
- Planètes à atmosphère fine de Dioxyde de Souffre ou de Dioxyde de Carbone
- Planètes rocheuses (Rocky)
- Température moyenne between 165 K and 190 K
Colored variants
Colored variant determined by the parent star type (see above, genus Stratum)
Stratum frigus

Description
This species of stratum forms broad interconnected ring structures, which are composed of narrow ridges to capture sunlight.
Conditions of occurrence
- Planets with thin Sulfur dioxide or Carbon dioxide atmosphere
- Rocky planets
- Mean temperature superior to 190 K
Colored variants
Colored variant determined by the parent star type (see above, genus Stratum)
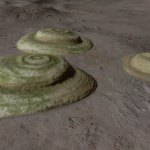
Stratum laminamus

Description
This particular stratum species gives the appearance of overlapping rock plateaus, each with narrow bands of colouration.
Conditions of occurrence
- Planets with thin Ammonia atmosphere
- Rocky planets
- Mean temperature superior to 165 K
Colored variants
Colored variant determined by the parent star type (see above, genus Stratum)
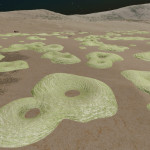
Stratum limaxus
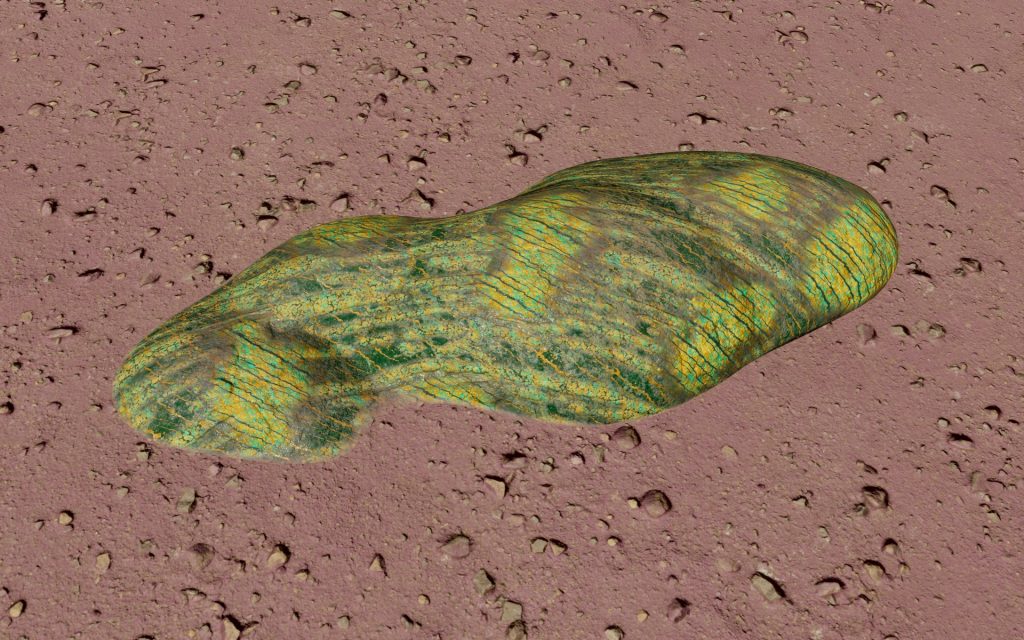
Description
This species of stratum appears as a series of unconnected ovoid sha pes across the ground, which are the protruding tips of the larger subterranean organism.
Conditions of occurrence
- Planets with thin Sulfur dioxide or Carbon dioxide atmosphere
- Rocky planets
- Mean temperature between 165 K and 190 K
Colored variants
Colored variant determined by the parent star type (see above, genus Stratum)
Stratum paleas
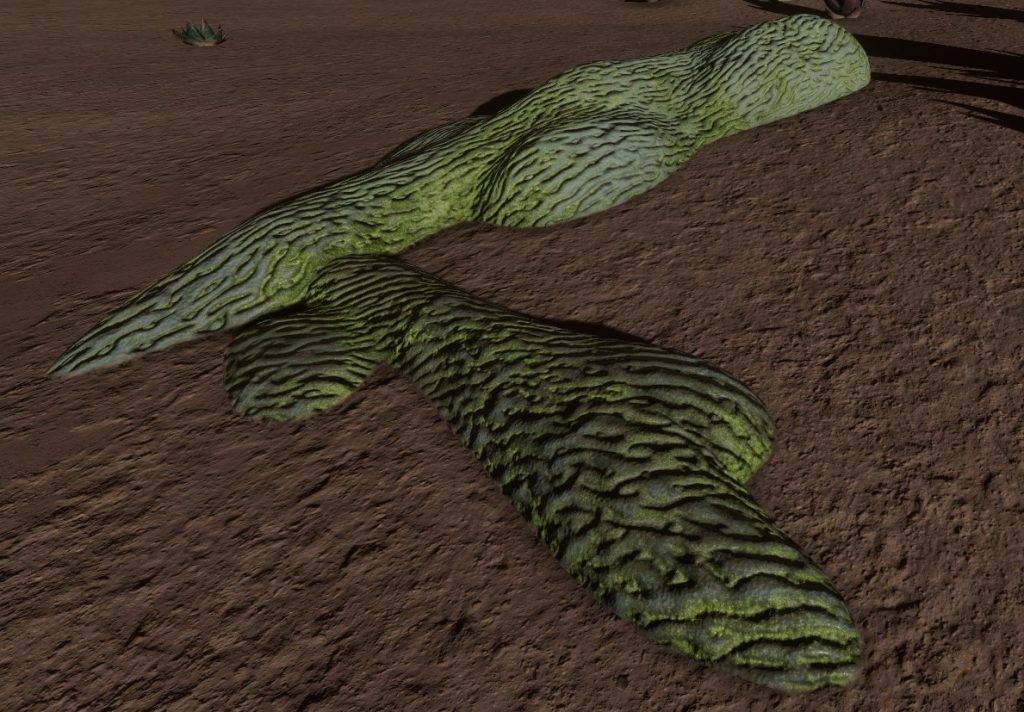

Description
A stratum that blends thick overlapping vines with irregular growths. with varying colours appearing in bands or streaks.
Conditions of occurrence
- Planets with thin Ammonia, Water or Carbon dioxide atmosphere
- Rocky planets
- Mean temperature superior to 165 K
Colored variants
Colored variant determined by the parent star type (see above, genus Stratum)
Stratum tectonicas
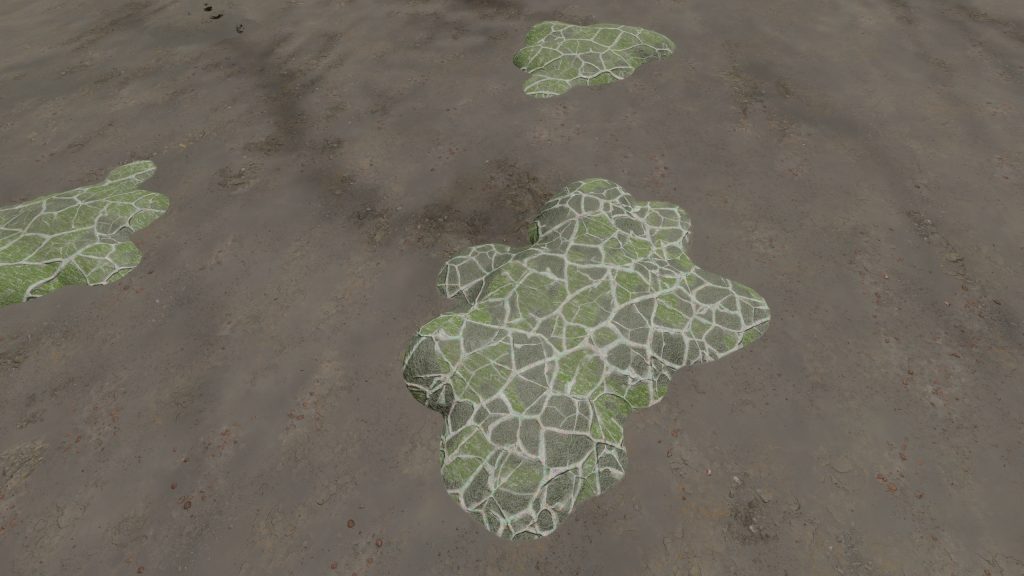

Description
A stratum species with a thick rock-like outer shell, covered with an irregular lattice of brighter cells that absorb sunlight for photosynthesis.
Conditions of occurrence
- Planets with thin atmosphere
- High Metal Content planets
- Mean temperature superior to 165 K
Colored variants
Colored variant determined by the parent star type (see above, genus Stratum)